EIAM vs CIAM | Understanding the Differences Between Employee and Customer Identity Management
Table of Contents
Introduction
As businesses increasingly adopt cloud services and SaaS applications, effective identity management for employees and customers has become increasingly critical. Identity management can be broadly categorized into two types: Employee Identity & Access Management (EIAM) for internal users and Customer Identity & Access Management (CIAM) for external customers. However, what are the key differences in their purposes, management approaches, and considerations when implementing these solutions?
Below, we'll provide a clear overview of the fundamental concepts and differences between EIAM and CIAM.
Overview of EIAM and CIAM
First, let's examine the target users and the essential characteristics and objectives that EIAM and CIAM should possess:
EIAM (Employee Identity and Access Management)
- Primary Target: Employees, partners, and other internal or business-related stakeholders
- Key Features and Objectives
- Enables employees to securely and efficiently access multiple corporate applications using a single set of credentials (ID/password)
- Focuses primarily on role-based access control, assigning permissions according to departmental structure and job functions
- Typically integrates with employee directories such as Active Directory or LDAP
CIAM (Customer Identity and Access Management)
- Primary Target: External users including service customers and members
- Key Features and Objectives
- Provides a mechanism for users (customers) to self-register accounts and access various services through a unified interface (self-service functionality)
- Often requires integration with social login providers (e.g., Google, Facebook) and multiple service interfaces (main service, user management dashboards like personal profiles, inquiry forms, etc.)
- Maintains a balance between "security" and "user experience (UX)," while also considering data protection and marketing utilization
What distinguishes employee-focused from customer-focused implementations?
Both EIAM and CIAM provide authentication and authorization functionality. What other aspects differentiate them? Here are three key points:
1. Number of actors
- EIAM: Primarily focuses on internal actors such as employees, partners, and administrative staff within the organization
- CIAM: Involves a much broader range of actors since it's used by unspecified numbers of customers/members, including support personnel and external authentication services. Additionally, among customers themselves, there are differences such as users with administrative privileges versus standard users. When deploying multiple services, the implementation complexity increases further.
2. Complexity of business workflows
- EIAM: Mainly revolves around lifecycle management ("onboarding to offboarding"). While there may be additional app additions or employee transfers, most workflows remain confined within the company
- CIAM: Requires consideration of multiple scenarios including customers' "registration → login → password reset → account termination" flow, as well as features like social login and single sign-on across multiple portals
3. Importance of user experience (UX)
- EIAM: Emphasizes operational efficiency and security. UI/UX requirements are typically limited to basic portal functionality. Security policy compliance and audit log acquisition are often prioritized over UI/UX considerations
- CIAM: Since users are typically customers, it directly impacts service satisfaction. User experience design is particularly critical here, including simple registration processes and seamless authentication flows. Additionally, operational efficiency in terms of user management may also be required
Summary
- EIAM is a system designed to streamline internal operations, with role-based authorization management being its primary focus
- CIAM is designed for customers and external users, making the balanced integration of UX and security its key challenge
- While both share the fundamental technologies of authentication and authorization, their operational designs and functional requirements vary significantly depending on the target audience and workflow
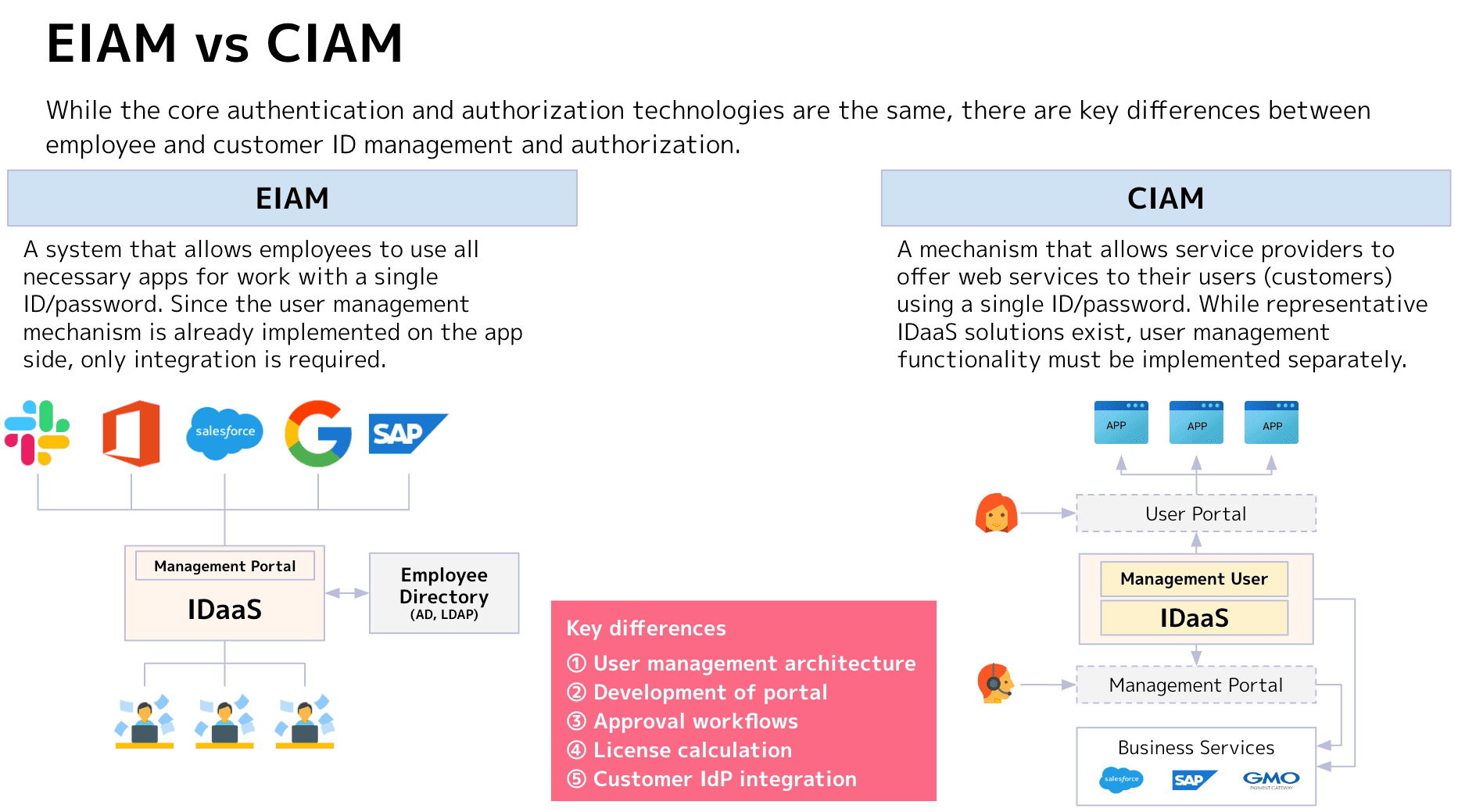
As shown in the following diagram, employee ID management typically involves relatively simple integration with existing directories and internal portals, whereas customer ID management requires consideration of additional actors and workflows, including user portals and external services

Next Steps
The key takeaway from what we've discussed here is the scope of services commonly referred to as IDaaS (short for Identity as a Service). For employee ID management (EIAM), with relatively simple actors and workflows, UI/UX requirements aren't as stringent, resulting in packaged solutions that often include portal functionality.
On the other hand, IDaaS solutions designed for customer ID management (CIAM) may include user management portals, but are often "developer-focused" services that lack operational management or user management portals. This often leads to situations where developers must perform operational tasks during implementation.
Understanding these differences between EIAM and CIAM and the scope of IDaaS services, we recommend starting with an analysis of your existing services—whether employee-facing or customer-facing—to properly organize the ID management workflows (customer journey) that will provide optimal user experiences.
.png&w=3840&q=75)